MySQL JOINS
MySQL JOINS
MySQL JOINS are used with SELECT statement. It is used to retrieve data from multiple tables. It is performed whenever you need to fetch records from two or more tables.
There are three types of MySQL joins:
- MySQL INNER JOIN (“or sometimes called simple join”)
- MySQL LEFT OUTER JOIN (“or sometimes called LEFT JOIN”)
- MySQL RIGHT OUTER JOIN (“or sometimes called RIGHT JOIN”)
MySQL Inner JOIN (“Simple Join”)
The MySQL INNER JOIN is used to return all rows from multiple tables where the join condition is satisfied. It is the most common type of join.
Syntax:
- SELECT columns
- FROM table1
- INNER JOIN table2
- ON table1.column = table2.column;
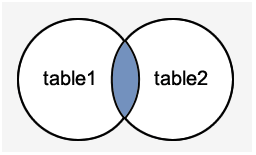
Image representation:
Let’s take an example:
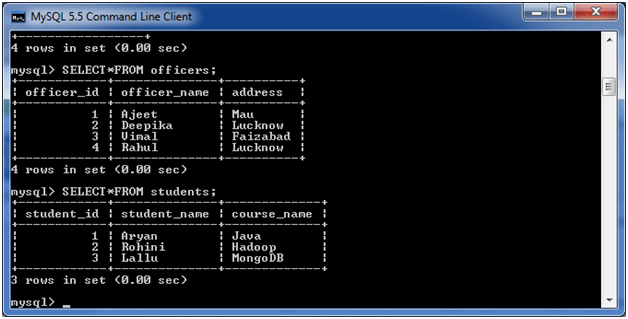
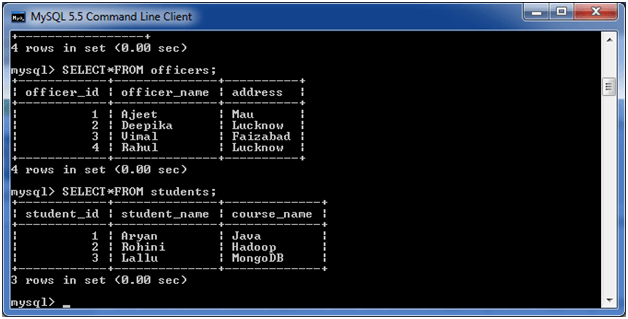
Consider two tables “officers” and “students”, having the following data.
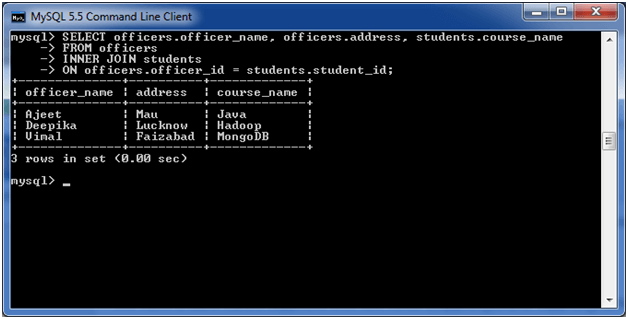
Execute the following query:
- SELECT officers.officer_name, officers.address, students.course_name
- FROM officers
- INNER JOIN students
- ON officers.officer_id = students.student_id;
Output:
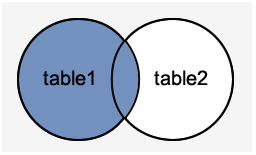
MySQL Left Outer Join
The LEFT OUTER JOIN returns all rows from the left hand table specified in the ON condition and only those rows from the other table where the join condition is fulfilled.
Syntax:
- SELECT columns
- FROM table1
- LEFT [OUTER] JOIN table2
- ON table1.column = table2.column;
Image representation:
Let’s take an example:
Consider two tables “officers” and “students”, having the following data.
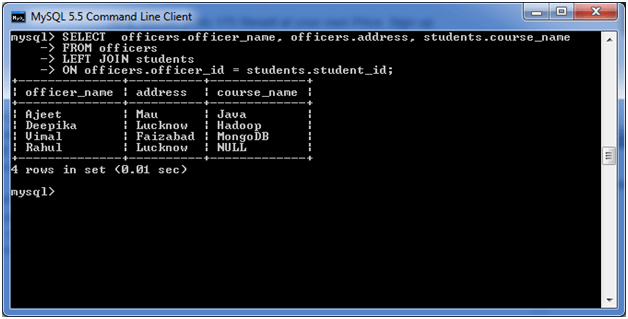
Execute the following query:
- SELECT officers.officer_name, officers.address, students.course_name
- FROM officers
- LEFT JOIN students
- ON officers.officer_id = students.student_id;
Output:
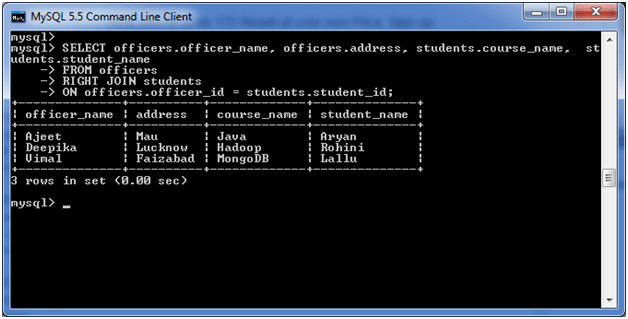
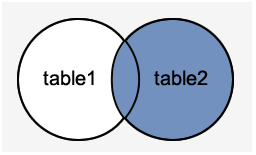
MySQL Right Outer Join
The MySQL Right Outer Join returns all rows from the RIGHT-hand table specified in the ON condition and only those rows from the other table where he join condition is fulfilled.
Syntax:
- SELECT columns
- FROM table1
- RIGHT [OUTER] JOIN table2
- ON table1.column = table2.column;
Image representation:
Let’s take an example:
Consider two tables “officers” and “students”, having the following data.
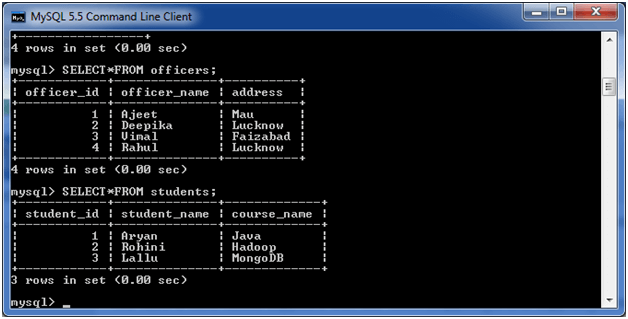
Execute the following query:
- SELECT officers.officer_name, officers.address, students.course_name, students.student_name
- FROM officers
- RIGHT JOIN students
- ON officers.officer_id = students.student_id;
Output: